
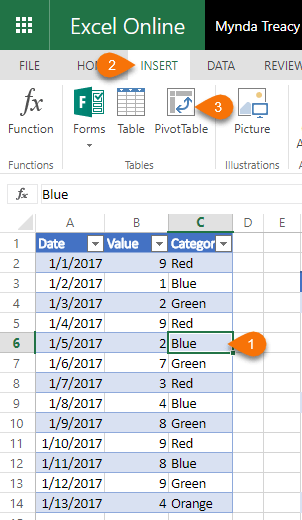
Note: the pivot table fields pane shows how fields were used to create a pivot table. The Filters area is used to apply global filters to a pivot table. To build a pivot table, drag fields into one the Columns, Rows, or Values area. Note all five fields are listed, but unused: However, when learning pivot tables, it's helpful to see both the source data and the pivot table at the same time.Įxcel also displays the PivotTable Fields pane, which is empty at this point. Note: there are good reasons to place a pivot table on a different worksheet. Click OK, and Excel builds an empty pivot table starting in cell H4. Override the default location and enter H4 to place the pivot table on the current worksheet:ģ. The default location for a new pivot table is New Worksheet.Ģ. Notice the data range is already filled in. To start off, select any cell in the data and click Pivot Table on the Insert tab of the ribbon:Įxcel will display the Create Pivot Table window. But generic data is good for understanding pivot tables – you don't want to get tripped up on on a detail when learning the fun parts. Excel Tables are a great way to build pivot tables, because they automatically adjust as data is added or removed. This data is perfect for a pivot table.ĭata in a proper Excel Table named "Table1". The sample data contains 452 records with 5 fields of information: Date, Color, Units, Sales, and Region. With experience, the pivot tables below can be built in about 5 minutes.

In this section, we'll build several pivot tables step-by-step from a set of sample data. To understand pivot tables, you need to work with them yourself. The beauty of pivot tables is they allow you to interactively explore your data in different ways. You can group data into categories, break down data into years and months, filter data to include or exclude categories, and even build charts. With very little effort (and no formulas) you can look at the same data from many different perspectives. However, unlike a static report, a pivot table provides an interactive view of your data. You can think of a pivot table as a report. Pivot tables can dramatically increase your efficiency in Excel.

Grab the sample data and give it a try. Learning Pivot Tables is a skill that will pay you back again and again. This article is an introduction to Pivot Tables and their benefits, and a step-by-step tutorial with sample data. With very little effort, you can use a pivot table to build good-looking reports for large data sets. Pivot tables are one of the most powerful and useful features in Excel.
PIVOT TABLES IN EXCEL UPDATE
And, if you want to update these custom pivot tables every time when you open a workbook, change the name of the macro to auto_open.Overview | Why Pivot? | Tips | Examples | Training Sub RefreshCustomPivotTable()Ĭhange the name of the pivot tables as per your workbook. If you have some specific pivot tables which you want to update then you can use below VBA code. Refresh Only Specific Pivot Tables with VBA
PIVOT TABLES IN EXCEL CODE
Sub RefreshCustomPivotTable()Ībove code will refresh all the pivot tables from your active worksheet and you can also assign this macro to a button to use in a single click. All you have to do is just use below-mentioned code. Yes, you can use VBA as well to refresh all pivot tables. VBA Code to Update All the Pivot Tables in a Single Click Go To Data Tab ➜ Tick Mark “Refresh Data When Opening A File”.Right click on it and select “PivotTable Options”.Select any of the pivot tables from your workbook.Below are the steps you can use to make al pivot tables auto refresh while opening a workbook.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
